DESCRIPTION-
The uterus is not a fixed organ. Minor variation in position in any direction occurs constantly with changes in posture, with straining, with full bladder or loaded rectum. Only when the uterus rests habitually in a position beyond the limit of normal variation, should it be called displacement.
RETROVERSION-
Definition-retroversion is the term used when the long axes of the corpus and cervix are in line and the whole organ turns backwards in relation to the long axis of the birth canal.
RETROFLEXION-
Retroflexion signifies a bending backwards of the corpus on the cervix at the level of internal os. The two conditions are usually present together and are loosely called retroversion or retrodisplacement.
DEGREES-
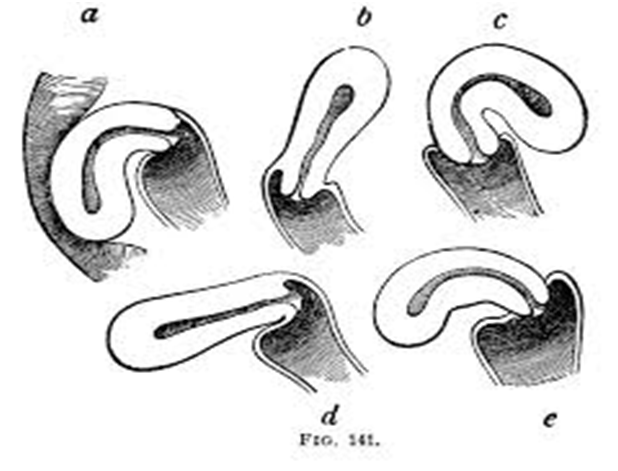
Conventionally, three degrees are-
FIRST DEGREE- The fundus is vertical and pointing towards the sacral promontory.
SECOND DEGREE- The fundus lies in the sacral hollow but not below the internal os.
THIRD DEGREE- The fundus lies below the level of the internal os.
CAUSES-
1]DEVELOPMENTAL
2]ACQUIRED
DEVELOPMENTAL
Retrodisplacement is quite common in fetuses and young children. Due to developmental defect, there is lack of tone of the uterine muscles. The infantile position is retained. This is often associated with short vagina with shallow anterior vaginal fornix.
ACQUIRED
1] PUERPERAL-
The stretched ligaments caused by childbirth fail to keep the uterus in its normal position. A subinvoluted bulky uterus aggravates the condition.
2] PROLAPSE
Retroversion is usually implicated in the pathophysiology of prolapsed which is mechanically caused by traction following cystocele .
3] TUMOR
Fibroid, either in the anterior or posterior wall produces heaviness of the uterus and hence it falls behind.
4] PELVIC ADHESION
Adhesions either inflammatory, operative or due to pelvic endometriosis pull the uterus posteriorly.
INCIDENCE
Retroversion is present in about 15-20% of normal women.
CLINICAL PRESENTION
1] Chronic premenstrual pelvic pain
2] Backache
3] Dyspareunia
4] Infertility
DIAGNOSIS
1] Bimanual examination
2] Speculum examination
3] Rectal Examination
The retrodisplacement may be confused with hard faecal mass in the rectum, small fibroid on the posterior wall of the uterus and small ovarian cyst in the pouch of Douglas.
PREVENTION
1] To empty the bladder regularly
2] To increase the tone of the pelvic muscles by regular exercise.
3] To encourage lying in prone position for half to one hour once or twice daily between 2 to 4 weeks postpartum.
COORECTIVE TREATMENT
1] PESSARY
2] SURGICAL
PESSARY-Use of pessary is almost obsolete in present day obstetric/gynecological practice.
Usually HODGE- SMITH Pessary is used. The pessary acts by stretching the uterosacral ligaments so as pull the cervix backwords.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
The principle of surgical correction is ventro suspension of the uterus by plicating the round ligaments of both the sides extra peritoneally to the under surface of the anterior rectus sheath .
This will pull the uterus forwards and maintains it permanently.