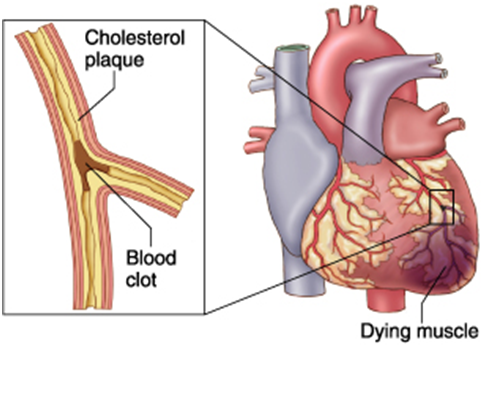
Definition :- MI is a cardio vascular diseases in which it is a life threatening condition characterized by the form of localized necrosis area within the myocardium usually caused reduced blood flow in a coronary artery.
INCIDENCE:- Each year US nearly 1 million people have MI and ¼ of these people dies from MI.
ETIOLOGY:- There are many causes or risk factors of MI:-
Ischemia, atherosclerosis, smoking, spasm of coronary artery, hypotension, aneamia.
Pathophysiology :-
Due to any etiological factors & Artherosclerosis
Inflammatory response
↓
Formation of lumen in vessels
↓
Narrowing of vessels
↓
Obsrruction in vessels
↓
Decrease in blood flow
↓
Rupture & haemorrhage into plaque
↓
Thrombous formation
↓
Ischemia
↓
Sudden cardiac death & MI
Clinical Features :- According to systems –
(1) Cardiovascular System –severe chest pain
–Discomfort
–palpitation
–Elevated B.P.
–Pulse Deficit
–Cardiogenic shock
(2)Respiratory Tract System –Dyspnea
–Shortness of breath
–Tachypnea
_ Pulmonary edema
(2) Gastro –intestinal Tract — Nausea & vomiting
(3) Genitourinary Tract _ Decrease urinary output
(4) Skin- _cool , pale appearance
(5) Neurological – —Anxiety
—Reastlessness
—Light headache
—Visual disturbance
—Altered speech
Diagnosis :-
(1) History collection about –smoking , alcoholism
–previous medical illness
(2) Physical examination —Inspection of skin( pale colour )
—Level of consciousness
(2) ECG ( Electro Cardio Graph )
(3) CBC (Complete Blood Count )
(4) Blood glucose level
(5) MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging )
(6) Serum Myoglobin & tropenin (protein found in myocardium)
Immediate / Emergency Managemant :-
–Ensure patients airway
–Administer oxygen therapy
–Provide IV fluid therapy
–Determine location & medicated for pain
–Obtain ECG & cardiac enzyme level
–Assess the need of thrombolytic therapy
–Monitor vital sign & prepare for CPR
Medical Management :–
(1) Administer Antiplatelets agents Example –Asprin , Ticlopidine
(2) Administer Beta –Blockers Example – Atenolol Timolol
(3) Administer Calcium – Channel Blockers Example – Nimodipine , Foledipine
(4) Administer Analgesic drug as per as docters order .
(5) Administer Cholesterol lowering agents .
(6) Administer Thrombolytic Therapy. Example :- Heparin
(7) Administer ACE ( Angiotenssive Converting Enzyme ) . Example- Captopril
Surgical Management :-
(1) PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty ) :- A ballon catheter inserted into the heart , in the blocked coronary artery is entered . The ballon on the catheter is inflated this procedure compress the plaque against the wall of artery this restoring the opening of artery .
(2) Coronary Atberectomy :- It is the removal of plaque from the coronary artery .
(3) Coronary Artery Bypass Graft :- Grafting of blocker of coronary artery .
Nursing Management :-
—Assess the condition of the patients .
—-Provide comfortable position & ventilation to the patients .
—-Monitor vital signs & diagnostic test .
—-Teach about to take low fat or cholesterol diet .
—- To teach about the stop smoking & alcoholism .
—-Teach about to maintain personal hygienic condition .
—- Maintain I/O chart of patient .
—-To give health education regarding the dietary pattern & healthy life style.
—-Instruct to avoid lifting of heavy load & heavy exercise .
—- Teach the client to avoid stressful condition .
—-Adm. the drug as per as physician orders .
—-Provide psychological support .