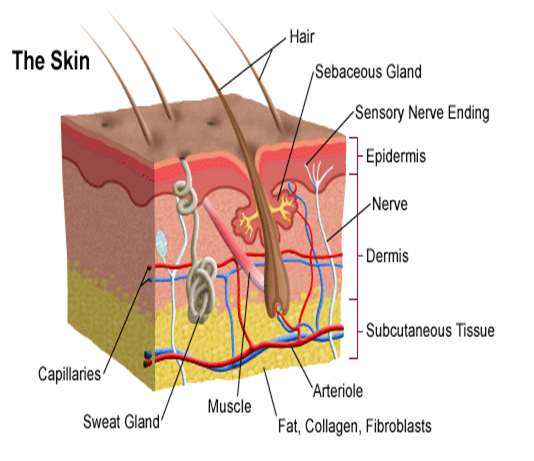
Description: SKIN: – The skin is the continuation of the membranous lining the body openings. It contains glands, hair, nails and consists of two layers.
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
EPIDERMIS:- The outer skin:-
It is the most superficial layer of the skin and made up of stratified epithelium. It is thickest on the palms of the hands and soles of feet. It contains no blood vessels and nerve cells and its nutrition is derived from the capillaries of the dermis. The Epidermis consists of five layers:
1. Stratum corneum:- It is the most superficial layer and it is made up of dead and highly Keratinised cells.
2. Stratum lucidum:- It is made up of clear non granulated cells.
3. Stratum granulosum:- It consist of granular cells and is about three cells layer thick.
4. Stratum spinosum:- It is 3-5 cells thick layers. The individual cells have a prickly appearance due to the fact that cytoplasmic processes come out from each cell to meet their fellow cytoplasmic strands.
5. Stratum germinativum :- It is the deepest layer of epidermis, made up of columnar cells which give rise to the new cells. It also contains melanocytes which synthesize a pigment called melanin.
DERMIS:- It is a thick and tough elastic layer of connective tissues which supports the hair.
1. Hair :- The hair develops from the hair follicles located in the epidermis.The part of the hair above is the shaft and the remainder ,the root. The colour of the hair depends on the amount of melanin pigment.
The Arrector pilli muscle is attached to the hair follicle.
2. Sebacious glands :- They develops from the hair follicles and usually open into it but in the face they may open into the exterior directly. They are most numerous in the skin of the scalp.
The secretion of the sebaceous glands is rich in oily substances that keep the hair soft.
3. Sweat glands: – They are basically a highly coiled tubular structure in the deeper part of the dermis. Sweat is synthesized by the coiled portion of the sweat glands from water, salt urea and other waste products. Two types of sweat glands are recognized: – Apocrine sweat glands and Ecrine sweat glands.
FUNCTIONS:-
1. PROTECTIVE FUNCTION:- Ultra violet rays of sun i.e. light rays less than 360 um in wavelength can cause damage to the skin producing sun burn and cancer of skin , called ultra violet radiation injury.
2. SENSE PERCEPTION:- Skin provides a sensory covering over the entire body.It contain nerve ending as well as various receptors for general sensation such as touch, pain, pressure and temperature.
3. TEMPERATURE REGULATION:- The different organs of the body by way of metabolism generate large quantities of heat which reaches the skin via blood .
4. WATER BALANCE:- The first layer of epidermis is such a membrane that it does not allow water to pass in and out.
5. Skin helps to eliminate waste products such as urea in the sweat.
JISHU BAIJU