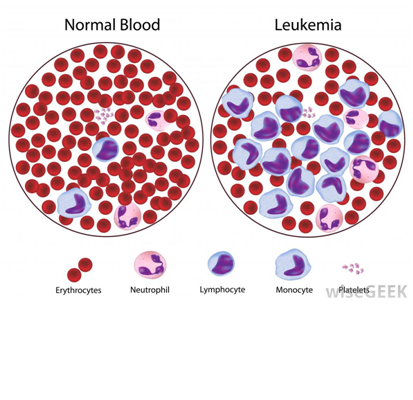
Description: – Leukemia ( Blood Cancer)
Definition: – It is a neoplastic proliferation of one particular cell l type and also affecting the bone morrow & lymphoid system which are all known as hematological neoplasm.
Increased white blood cells is called as Blast cells.
The term leukemia refers to an increase level of leukocytes in the circulation.
Etiology:- 1. Genetic factor(Abnoemal chromosomalmay increase the risk for leukemia such as down syndrome or trisomy 21.)
2. HTLV-I (The presence of primary immune deficiency &infection with the Human T-
lymphocyte Virus Type-I)
3. Exposure to chemical & benzene
4. Exposure to radiation
5. Smoking
6. Chemotherapy or Radiation
Classification: It is clinically submitted into a variety of large group.
A. Acute Leukemia: It is characterized by the rapid increase of immature blood cells. This crowding makes the bone marrow unable to produce healthy blood Cells. The result is a massive accumulation of immature, nonfunctional cells or blast in the bone marrow & in the other Organ.
B. chronic Leukemia: It is distinguish by the excessive build up of relatively mature but still abnormal wbc taking the month or years to progress.
BONE MARROW forming cell
Sign & Symptom:-
A. Aneamia
B. Seizures
C. Headache
D. Spleenomegaly
E. Bleeding
F. Fever
G. Weight loss
H. Fatigue
I. Sweating
J. Abdominal Pain
K. Joint Pain
L. Tiny Red Spot on Skin
Diagnostic Findings:-
A.Bone marrow biopsy
B.Cytogenetics
C.PCR( Polymer chain Reaction)
D.Lumber Puncture ( Spinal Tab )
E.CBC
F. FNAC( Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology)
Treatment:-
A.Chemotherapy
B.Drug:- Doxorubicin, Cisplastin. Monoclonal Antibodies, Interferon Alpha ,Rituximab
C.Radiation Therapy
D. Blood Transfusion
E. Bone marrow transplantation
F. stem cell transplantation
G.Interferon Alpha Therapy With or Without chemotherapy
H. Use of specific Tyrosin kinase Inhibitotrs
Tarun Mudgul